Both the flu and covid are infectious diseases and very contagious. Visit your Primary Care Provider for personal guidance if you suspect you have either.
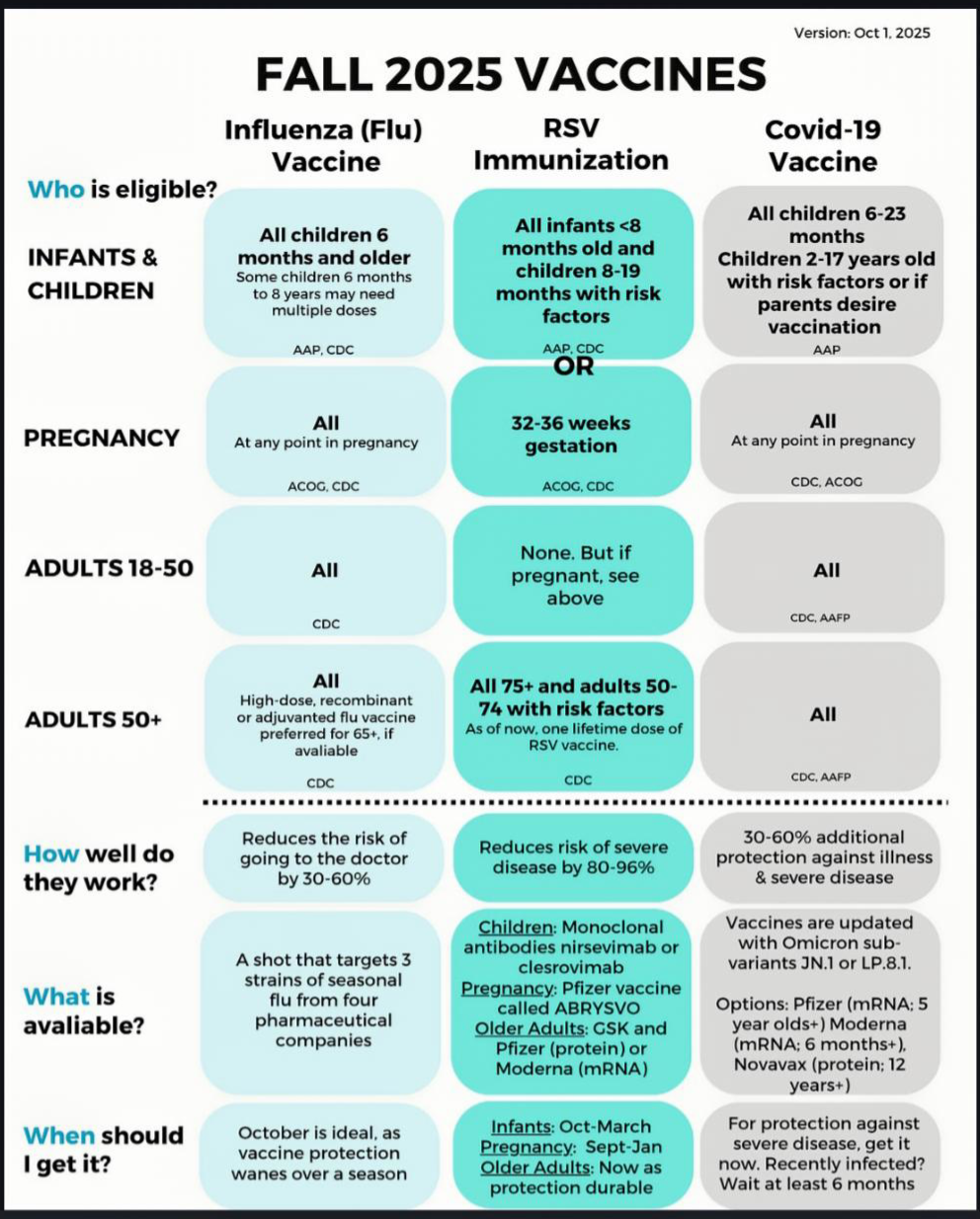
Vaccinations help prevent and lessen the severity of illness. Refer to the most recent fall vaccine recommendations.

Flu
Influenza (flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs. Some people, such as people 65 years and older, young children, and people with certain health conditions, are at higher risk of serious flu complications. There are two main types of influenza (flu) viruses: types A and B. The influenza A and B viruses that routinely spread in people (human influenza viruses) are responsible for seasonal flu epidemics each year.
For more information on the flu, please visit the CDC About flu website.
Tested positive for the flu? Follow the CDC guidelines.

Covid 19
COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019) is a disease caused by a virus named SARS-CoV-2. It can be very contagious and spreads quickly. Over one million people have died from COVID-19 in the United States.
COVID-19 most often causes respiratory symptoms that can feel much like a cold, the flu, or pneumonia. COVID-19 may attack more than your lungs and respiratory system. Other parts of your body may also be affected by the disease. Most people with COVID-19 have mild symptoms, but some people become severely ill.
Some people including those with minor or no symptoms will develop Post-COVID Conditions – also called “Long COVID.”
For more information on COVID, please visit the CDC website.
Covid-19 will now be treated like other common respiratory illnesses. For more information and guidance, visit the CDC respiratory illness website.

RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus)
RSV can be dangerous for certain adults.
Risk factors that increase the risk for severe RSV
Adults at highest risk for severe RSV disease include:
Symptoms in infants and young children
RSV may not be severe when it first starts. However, it can become more severe a few days into the illness. Early symptoms of RSV may include:
RSV in very young Infants
Infants who get RSV almost always show symptoms. This is different from adults, who can sometimes get RSV and not have any symptoms. In very young infants (less than 6 months old), the symptoms of RSV may include:
Many infants will not have a fever with RSV infection.
Severe RSV
Most of the time RSV causes a mild, cold-like illness, but it can also cause severe illness such as:
Two to three out of every 100 infants under 6 months are hospitalized with RSV every year. Those who are hospitalized may require oxygen, IV fluids (if they aren't eating and drinking), and mechanical ventilation (a machine to help with breathing). Most improve with this type of supportive care and are discharged in a few days.
When to seek emergency care
Seek medical attention if your child is having difficulty breathing, not drinking enough fluids, or experiencing worsening symptoms.
For the complete list of medical conditions and risk factors for severe RSV disease, see RSV Clinical Overview.